Abstract
Background: Relapsed or refractory MCL (RR-MCL) is an area of significant unmet need, especially in the presence of high-risk features such as TP53 aberrancy, which is associated with treatment resistance and/or early treatment failure with current therapies. Preclinical and clinical data support the potential role of ibrutinib in apheresis product fitness, cytokine release syndrome (CRS) abrogation, and CAR-T expansion. TARMAC is an investigator-initiated multi-centre trial assessing the efficacy and safety of a time-limited combination of ibrutinib and the anti-CD19 CAR-T product tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel) in RR-MCL.
Methods: Patients (pts) had a centrally confirmed diagnosis of RR-MCL with radiologically measurable or morphologic marrow disease, adequate organ function, and no prior CAR-T. Prior BTKi exposure was allowed. Ibrutinib (560mg daily) was commenced at least 7 days prior to leukapheresis and continued throughout optional bridging, lymphodepletion (fludarabine 25mg/m2 and cyclophosphamide 250mg/m2 each daily x 3) and for 6 months after tisa-cel infusion. Molecular profiling included: FISH for t(11;14) and del(17p); and next generation sequencing. Measurable residual disease (MRD) on peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) samples during treatment and follow up was assessed by flow cytometry (sensitivity between 10-4 & 10-5), and high throughput immunoglobulin sequencing (IgHTS) (sensitivity between 10-5 & 10-6; Adaptive Biotechnologies). CAR-T quantitation was by digital PCR. Immunologic profiling of baseline and on-treatment PB samples was described using spectral flow cytometry. The primary endpoint was complete response (CR) rate by Lugano criteria at month 4 (M4) after tisa-cel and key secondary endpoints included safety, rates of MRD negativity, ORR, PFS, DOR and OS.
Results: Twenty-one pts were enrolled, one withdrew consent, and 20 were infused. The median age was 66 years (range 41-74y), 75% were male. Median prior therapies was 2 (range 1-5 lines); 55% had undergone prior autologous transplantation. 10 pts (50%) had prior BTKi, 9 were refractory. 4 pts required bridging: venetoclax (n=1) or chemotherapy (n=3). Genomic results were available for 18 pts with 8/18 (44%) demonstrating one or more TP53 mutations. Eight pts had del(17p), including 7 of the 8 pts also demonstrating a TP53 mutation, suggestive of biallelic TP53 dysfunction.
Ibrutinib therapy was well tolerated with 97% mean dose intensity achieved. After tisa-cel infusion, 75% of pts experienced CRS; 11/15 (73%) grade 1-2, 4/15 (27%) grade 3 with no grade 4 events. One episode of ICANS (grade 2) was observed with complete resolution. Atrial fibrillation was observed in one pt associated with infection. Overall grade 3 and 4 toxicities were seen in 75% and 50% of pts. There were no deaths.
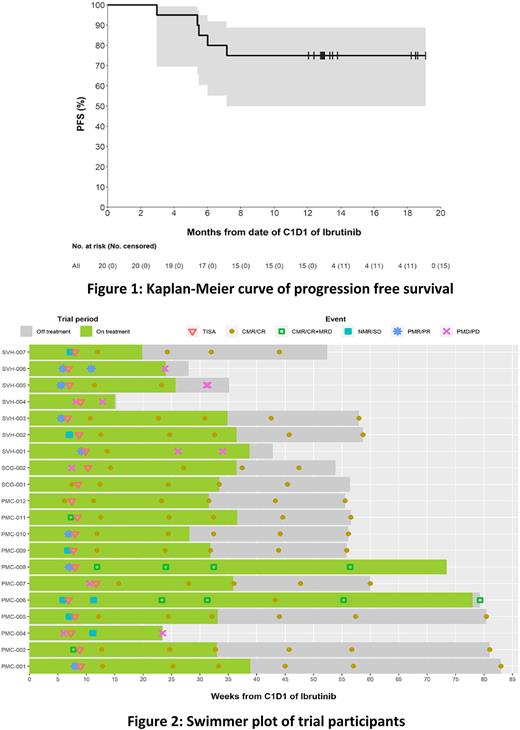
The median follow-up was 13.0 months (range 3.5-21.4). The ORR was 90% (CR 85%, PR 5%), with median time to best response of 1 month (range 1-4). At M4 post-infusion, 16 pts (80%) were in CR and 4 had progressed. Fourteen pts (70% of all pts) demonstrated MRD negativity in PB and BM by flow cytometry; 8/14 were also negative by IgHTS. The CR rate (CRR) at M4 in BTKi naïve and exposed populations were 90% and 70% respectively. Median DOR has not been reached, with an estimated 83% of responding pts retaining their response at 12 months. The estimated PFS rates at 12 months were 75% and OS 100% (Figure 1). Response rates and durability of responses were similar between TP53 wildtype and TP53 mutated pts, with CRR at 12 months of 78% and 71% respectively.
Pts in MRD-negative CR at M4 by flow cytometry (deep responders) demonstrated higher peak CAR-T (Cmax 25.4 vs 8.5 CAR19 copies/1000 RPP30; p=0.032) and CAR-T area under the curve to day 28 (356 vs 141 CAR19 copies/1000 RPP30 x days; p=0.039) compared with progressors or MRD-positive pts. Immunologic profiling of deep responders demonstrated significantly lower baseline and pre-leukapheresis CD8+/HLA-DR-/PD1+ Temra populations, consistent with a less exhausted pre-manufacture T-cell phenotype.
Conclusion: This time-limited combination of ibrutinib and tisa-cel is a highly effective treatment in RR-MCL leading to a high rate of durable responses, irrespective of prior BTKi exposure and/or TP53 status. Deep responses were correlated with more robust CAR-T expansion and a less exhausted baseline T-cell state. The safety profile was favourable.
Disclosures
Minson:Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding. Hamad:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Cheah:Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Merck Sharp & Dohme: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Eli Lilly and Company: Consultancy, Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Beigene: Consultancy, Honoraria. Tam:LOXO: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Beigene: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Blombery:Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy, Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria. Lade:EUSA Pharma: Consultancy. Ritchie:BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; MSD: Honoraria. Koldej:CRISPR Therapeutics: Research Funding. Anderson:Roche: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Walter and Eliza Hall Institute: Current Employment, Other: Employee of the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute which recieves milestone payments in relation to venetoclax to which I am entitled to a share. Khot:BMS: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Mundipharma: Honoraria; Novartis: Other: Travel Grant. Seymour:Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genor Biopharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Dickinson:Roche, BMS, Novartis, Kite, Gilead, NKARTA, AdiCet Bio, Interius, Janssen, MSD: Consultancy; Roche, BMS, Novartis, Kite, Gilead, NKARTA, AdiCet Bio, Interius, Janssen, MSD, Amgen: Honoraria; Roche, Novartis, Kite, Gilead, MSD, Takeda, Celgene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal